Table of Contents
Meaning of International Arbitrage
International Arbitrage is the process of selling and buying foreign securities and ADRs simultaneously to take advantage of imperfect pricing in different international markets.
Arbitrage is the process of simultaneously selling and buying the same assets or commodities in order to profit from imperfect market pricing. An arbitrager buys the security from one market at a lower price and sells it at a higher price in another market for a riskless advantage.
However, if the market is in equilibrium, then there is no space for arbitrage. Therefore, for arbitrage, there must be a price mismatch for the same asset in the market.
Types of International Arbitrage
International Arbitrage can be further divided into components as mentioned below-
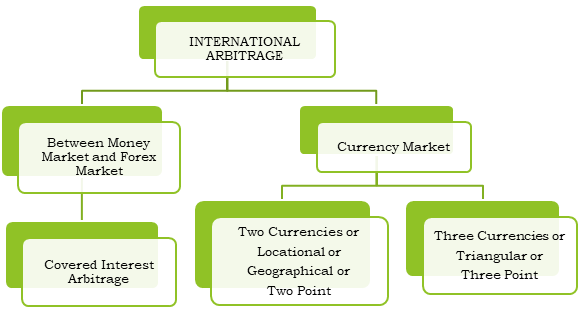
Covered Interest Arbitrage (CIA)
This is the first international arbitrage. Under the CIA, arbitrageurs take advantage of the interest rate differential between two countries by hedging themselves under forward contracts to earn riskless profits.
The term “covered” means hedging through a forward contract in the forex market against fluctuations in the exchange rate, and the term “interest arbitrage” means taking advantage of an interest differential between two countries.
This international arbitrage is possible only when Interest Rate Parity (IRP) is not valid. That means the interest differential is not equal to a percentage of the spread between two currencies.
Now let’s understand this international arbitrage in simple words. Under this international arbitrage, there would be two scenarios, and our action would be based on the under or overpricing of the base currency.
Scenario I – Base Currency Overpriced in Forex Market
- To profit from overpricing, an arbitrager will sell (go short on) the base currency in the Forex market.
- In this case, to cover the above position, an arbitrager has to deposit the base currency (long position) in the Money Market.
- To deposit the base currency, he must borrow in the money market in price currency and convert the borrowed price currency into base currency for deposit.
Scenario II – Base Currency Under-priced in Forex Market
- An arbitrager will buy (take a long position in) the base currency in the Forex market to take advantage of under pricing.
- In this case, an arbitrager must borrow (take a long position) in the base currency in the money market to cover the above position.
- After borrowing in base currency, he will deposit it in price currency in Money Market by converting the borrowed base currency into price currency.
If you want to see example and other discussion about this international arbitrage then click here
Two Point Arbitrage
The second type of International Arbitrage is two-point arbitrage. Buying a currency in one market and selling it at a higher price in another, geographically different market is called two-point arbitrage.
Normally, the exchange rate for a given currency should be the same in every part of the world. However, due to some discrepancies in the market, the prices might differ in various markets, and in such cases, the arbitrageur would buy the currency in the market where its price is lower and then sell the currency in the market where its price is higher.
If the exchange rate differential is higher than the transaction cost, an arbitrage profit can be made.
Do Remember:
What would be no arbitrage condition for two currencies?
- Bid rate of one bank = ask rate of another bank
- Ask rate of one bank is above bid rate of another bank
If you want to see example and other discussion about this international arbitrage then click here
Triangular Arbitrage or Three Point Arbitrage
This is the third one under the “International Arbitrage” category. Triangular arbitrage is the result of a mismatch in the exchange rates of three currencies. Under this international arbitrage mechanism, arbitrageurs take advantage of the discrepancy among three different currencies in the foreign exchange market. Triangular arbitrage may exist only when the derived or implied cross rate is not equal to the quoted exchange rate.
Suppose there are three currencies, i.e. ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’ then under this international arbitrage, if there is any arbitrage opportunity, the arbitrageur will sell currency ‘A’ and buy currency ‘B’, then sell currency ‘B’ and buy currency ‘C’ and then sell currency ‘C’ and buy currency ‘A’. It means triangular arbitrage involve three trade that’s why it is known as triangular arbitrage.
Calculation Step for this international arbitrage
- Calculate implied or derived cross rate
- Compare implied cross rate with quoted exchange rate and select higher bid and lower ask
- Calculate profit which is difference of above selected rates
- Then start triangular arbitrage by selling that currency which is reported in profit.
- Sell 1 unit of ‘A’ and buy ‘B’ * Sell 1 unit of ‘B’ and buy ‘C’ * Sell 1 unit of ‘C’ and buy ‘A’ = ****** ( – ) Initial Investment 1 = Profit
If you want to see example and other discussion about this international Arbitrage then click here
Benefits of International Arbitrage
International arbitrage is a financial strategy that involves taking advantage of price differences between markets in different countries. Although it can be a complex and risky practice, there are several benefits to international arbitrage that make it an attractive option for many investors.
Increased Profit Opportunities
One of the primary benefits of international arbitrage is the potential for increased profit opportunities. By identifying price discrepancies between markets, investors can buy assets in one market and sell them in another at a higher price, pocketing the difference as profit. In an international context, currency exchange rates can also create additional price discrepancies, further increasing the potential for profit.
Diversification
International arbitrage can also provide investors with diversification benefits. By investing in assets in different countries, investors can reduce their exposure to risks associated with a single market or currency. This can help to minimize losses and protect against market volatility.
Efficient Market Allocation
International arbitrage can also help to promote efficient market allocation. By exploiting price discrepancies, investors can help to equalize prices between markets and ensure that assets are allocated to their most productive uses. This can help to increase economic efficiency and promote overall economic growth.
Access to Unique Opportunities
International arbitrage can also provide investors with access to unique investment opportunities that may not be available in their home market. For example, an investor in the United States may be able to purchase shares in a company that is not listed on any U.S. exchanges but is trading at a lower price on a foreign exchange.
Hedging Against Risk
Finally, international arbitrage can also serve as a hedging strategy against certain types of risk. For example, if an investor holds a portfolio of assets denominated in a particular currency, they may use international arbitrage to hedge against currency risk by taking advantage of price differences in other markets.
In conclusion, international arbitrage can be a complex and risky financial strategy, but it also offers several benefits for investors. From increased profit opportunities and diversification to promoting efficient market allocation and accessing unique investment opportunities, international arbitrage can be a powerful tool for investors looking to maximize their returns and minimize their risks. However, it is important to remember that international arbitrage requires careful research, analysis, and execution in order to be successful.
Conclusion
In conclusion, international arbitrage can be a valuable financial strategy for investors looking to take advantage of price discrepancies between markets in different countries. The benefits of international arbitrage include increased profit opportunities, diversification, efficient market allocation, access to unique investment opportunities, and hedging against risk. However, it is important for investors to approach international arbitrage with caution and careful research, analysis, and execution in order to minimize risk and maximize returns. Overall, international arbitrage can be a powerful tool for sophisticated investors who are willing to do the necessary legwork to identify and capitalize on price discrepancies in global markets.




